PZU Group's risk profile

Major risks in the PZU Group
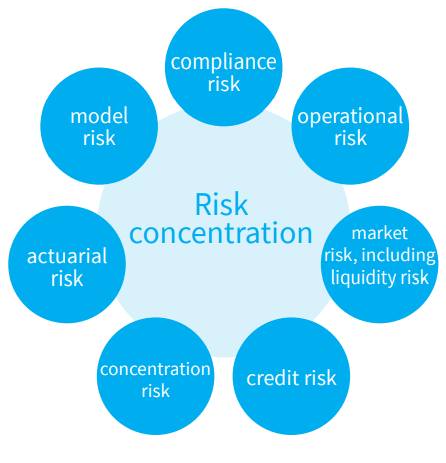
The major risks to which the PZU Group is exposed include the following: actuarial risk, market risk, credit risk, concentration risk, operational risk, model risk and compliance risk.
The major risks associated with the operation of Alior Bank and Bank Pekao include the following risks: credit risk (including the risk of loan portfolio concentration), operational risk and market risk (involving interest rate risk, FX risk, commodity price risk and financial instrument price risk).
The overall risk of the banking sector entities accounts for approximately 35% of the PZU Group’s total risk (Q3 2020), while the largest contribution is in credit risk.
In connection with the COVID-19 pandemic, increased risk was recorded in selected areas, especially mortality risk, interest rate risk, liquidity risk and credit risk.
In 2020, initiatives were undertaken to improve the identification, measurement, assessment and monitoring of the risks associated with sustainable development, in particular with climate changes. The main risks in this area - transformation risk and physical risk, are managed as part of individual risk categories specified below in this Report.
Physical risk is risk to the company that arise from the physical effects of climate change and include: acute physical risk (e.g. storms, fires) and chronic physical risk (e.g. rising sea level). Transition risk is risk that arise from the transition to a low-carbon and climate-resilient economy on climate change and covers policy risk, legal, technological, market and reputational.
Actuarial risk
This is the likelihood of a loss or an adverse change in the value of liabilities under the existing insurance contracts and insurance guarantee agreements, due to inadequate assumptions regarding premium pricing and creating technical provisions.
Risk identification commences with a proposal to develop an insurance product and continues until the expiry of the related liabilities. The identification of actuarial risk is performed, among others, as follows:
- an analysis of the general terms and conditions of insurance with respect to the accepted risk and compliance with the existing laws;
- an analysis of the general/specific terms and conditions of insurance or other model agreements with respect to the relevant actuarial risk being undertaken;
- recognizing the potential risks related to a given product to measure and monitor them at a later time;
- analyzing the impact exerted by the introduction of new insurance products on capital requirements and risk margin computed using the standard formula;
- verifying and validating modifications to insurance products;
- an assessment of actuarial risk with reference to similar existing insurance products;
- monitoring of existing product;
- analyzing the policy of underwriting (assessment of the risk accepted for insurance), tariffs, technical provisions and reinsurance and the claims and benefits handling process.
The assessment of actuarial risk consists in the identification of the degree of the risk or a group of risks that may lead to a loss, and in an analysis of risk elements in order to make an underwriting decision.
The measurement of actuarial risk is performed using:
- an analysis of selected ratios;
- the scenario method - an analysis of impairment arising from an assumed change in risk factors;
- the factor method - a simplified version of the scenario method, reduced to one scenario per risk factor;
- statistical data;
- exposure and sensitivity measures;
- application of the expertise of the Company’s employees.
The monitoring and control of actuarial risk includes a risk level analysis by means of a set of reports on selected ratios.
Reporting aims to ensure effective communication regarding actuarial risk and supports management of actuarial risk at various decision-making levels – from an employee to the supervisory board. The frequency of each report and the scope of information provided therein are tailored to the needs at each decision-making level.
The management actions contemplated in the actuarial risk management process are performed by doing the following:
- defining the level of tolerance for actuarial risk and monitoring it;
- business decisions and sales plans;
- calculation and monitoring of the adequacy of technical provisions;
- tariff strategy, monitoring of current estimates and assessment of the premium adequacy;
- the process of assessment, valuation and acceptance of actuarial risk;
- application of tools designed to mitigate actuarial risk, including in particular reinsurance and prevention.
Moreover, mitigation of the actuarial risk inherent in current operations is supported by:
- defining the scopes of liability in the general / specific terms and conditions of insurance or other model agreements
- co-insurance and reinsurance;
- application of an adequate tariff policy;
- application of the appropriate methodology for calculating technical provisions;
- application of an appropriate procedure to assess underwriting risk;
- application of a correct claims or benefits handling procedure;
- sales decisions and plans;
- prevention.
As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, an increase in the mortality risk was recorded. It was taken into account in the regular business processes and the risk is subject to regular monitoring and control.
Market risk, including liquidity risk
Market risk is understood as the risk of a loss or an adverse change in the financial situation resulting, directly or indirectly, from fluctuations in the level and in the volatility of market prices of assets, credit spread, as well as value of liabilities and financial instruments.
The risk management process for the credit spread and concentration risk has a different set of traits from the process of managing the other sub-categories of market risk and has been described in a subsequent section (Credit risk and concentration risk) along with the process for managing counterparty insolvency risk.
The market risk in the PZU Group originates from three major sources:
- operations associated with asset and liability matching (ALM portfolio);
- operations associated with active allocation, i.e. designating the optimum medium-term asset structure (AA portfolios);
- banking operations – in conjunction with them the PZU Group has a material exposure to interest rate risk.
Numerous documents approved by supervisory boards, management boards and relevant committees govern investment activity in the PZU Group entities.
Market risk identification consists in the identification of actual and potential sources of this type of risk. For assets, the identification of risk begins with the decision to commence transactions in a given type of financial instrument. Units that make a decision to start entering into such transactions draw up a description of the instrument containing, in particular, a description of the risk factors. They convey this description to the unit responsible for risk that identifies and assesses market risk on that basis.
The identification of market risk associated with insurance liabilities commences with the process of developing an insurance product. It involves identification of the relationship between the cash flows generated by that product and the relevant market risk factors. The identified market risks are subject to assessment using the criterion of materiality, specifying whether the materialization of risk entail a loss capable of affecting the financial condition.
Market risk is measured using the following risk measures:
- VaR, or value at risk, a measure quantifying the potential economic loss that will not be exceeded within a period of one year under normal conditions, with a probability of 99.5%; formuły standardowej;
- standard formula;
- exposure and sensitivity measures;
- accumulated monthly loss.
In the case of banking entities suitable measures are employed in accordance with the regulations applicable to this sector and best market practices.
Market risk measurement is divided into stages, in particular:
- collection of information on assets and liabilities that generate market risk,
- calculating the value of risk.
The risk measurement is performed:
- daily – for exposure and sensitivity measures of the instruments in systems used by particular PZU Group companies,
- monthly – when using the value at risk model for market risk or a standard formula.
Monitoring and control of market risk involves an analysis of the level of risk and of the utilization of the designated limits.
Reporting involves communicating to the various decisionmaking levels information concerning the level of market risk and the results of monitoring and controlling it. The frequency of each report and the scope of information provided therein are tailored to the information needs at each decision-making level.
Management actions in respect to market risk involve in particular:
- execution of transactions serving the purpose of mitigation of market risk, i.e. selling a financial instrument, closing a position on a derivative, purchasing a derivative to hedge a position;
- diversification of the assets portfolio, in particular with respect to market risk categories, maturities of instruments, concentration of exposure in one entity, geographical concentration;
- setting market risk restrictions and limits.
The application of limits is the primary management tool to maintain a risk position within the acceptable level of risk tolerance. The structure of limits for the various categories of market risk and also for the various organizational units is established by appointed committees in such a manner that the limits are consistent with risk tolerance as agreed by the management boards of the subsidiaries. Banking sector entities are in this respect subject to additional requirements in the form of sector regulations.
In connection with the COVID-19 pandemic, the banking sector in Poland recorded a significant decrease in net interest income. This affected also the banks from the PZU Group. The reduction of the NBP reference interest rate in total by 140 bp in the first half of 2020 brought down the net interest margin (NIM) in the sector.
In connection with recognizing additional provisions in PZU Życie in Q2 2020 and taking into account the current interest rate levels in the business processes, in the short term the risk associated with low interest rates in the PZU Group’s insurance segment is not perceived as significant. The risk is monitored and analyzed on an ongoing basis to ensure proper adaptation of the investment portfolio structure.
Financial liquidity risk means the possibility of losing the capacity to settle, on an ongoing basis, the PZU Group’s liabilities to its clients or business partners. The liquidity risk management system aims to maintain the capacity of fulfilling the entity’s liabilities on an ongoing basis. Liquidity risk is managed separately for the insurance part and the banking part.
The risk identification involves analysis of the possibility of occurrence of unfavorable events, in particular:
- shortage of liquid cash to satisfy the current needs of the PZU Group entity,
- lack of liquidity of financial instruments held,
- the structural mismatch between the maturity of assets and liabilities.
Risk assessment and measurement involve estimation of the shortage of cash to pay for liabilities. The risk estimate and measurement is carried out from the following perspectives:
- liquidity gaps (static, long-term financial liquidity risk) – by monitoring a mismatch of net cash flows resulting from insurance contracts executed until the balance sheet date and inflows from assets to cover insurance liabilities in each period, based on a projection of cash flows prepared for a given date;
- potential shortage of financial funds (medium-term financial liquidity risk) – through analysis of historical and expected cash flows from the operating activity;
- stress tests (medium-term financial liquidity risk) – by estimating the possibility of selling the portfolio of financial investments in a short period to satisfy liabilities arising from the occurrence of insurable events, including extraordinary ones;
- current statements of estimates (short-term financial liquidity risk) – by monitoring demand for cash reported by business units of an insurance undertaking in the PZU Group by the date defined in regulations which are in force in that entity.
The banks in the PZU Group employ the liquidity risk management metrics stemming from sector regulations, including Recommendation P issued by the Polish Financial Supervision Authority.
To manage the liquidity of the banks in the PZU Group, liquidity ratios are used for different periods ranging from 7 days, to a month, to 12 months and to above 12 months.
Within management of liquidity risk, banks in the PZU Group also analyze the maturity profile over a longer term, depending to a large extent on the adopted assumptions about development of future cash flows connected with items of assets and equity and liabilities. The assumptions take into consideration:
- stability of equity and liabilities with indefinite maturities (e.g. current accounts, cancellations and renewals of deposits, level of their concentration);
- possibility of shortening the maturity period for specific items of assets (e.g. mortgage loans with an early repayment option);
- possibility of selling items of assets (liquidity portfolio).
Monitoring and controlling financial liquidity risk involves analyzing the utilization of the defined limits.
In connection with the COVID-19 pandemic, banks in Poland, including the banks from the PZU Group, experienced overliquidity in 2020. The pandemic caused a major disruption of the existing simple model involving transfer of funds from bank deposits to finance the economy. In the banks’ balance sheets, the inflow of deposits remains undisrupted but the outflow is not routed mainly to finance the economy but to purchase of securities issued and guaranteed by the State Treasury. This results in an increase of debt securities and, consequently, increase of liquidity, in the banks’ balance sheets. Reduction of the lending activity results from the banks’ restrictive lending policy and, at the same time, clients’ aversion to incurring debt in unpredictable conditions. The banks’ liquidity was additionally strengthened by the reduction of the NBP reserve requirement from 3.5% to 0.5% as of the end of April 2020.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the liquidity of the PZU Group’s insurance segment in 2020 should be classified as low. An increase in the number of deaths (mortality rate) was observed, which could result from, among other things, the hindered access to health care and COVID-19 related complications. However the situation did not significantly impact PZU Group’s liquidity risk. In 2020 there were no grounds to take extraordinary management actions regarding liquidity risk in connection with the COVID-19 pandemic. As part of routine management actions regarding liquidity risk in 2020, the PZU Group constantly monitored the level of available liquid funds and the current utilization of liquidity limits.
Liquidity risk reporting involves communicating the level of financial liquidity to various decision-making levels. The frequency of each report and the scope of information provided therein are tailored to the information needs at each decision-making level.
The following measures aim to reduce financial liquidity risk:
- maintaining cash in a separate liquidity portfolio at a level consistent with the limits for the portfolio value;
- maintaining sufficient cash in a foreign currency in portfolios of investments earmarked for satisfying insurance liabilities denominated in the given foreign currency;
- provisions of the Agreement on managing portfolios of financial instruments entered into between TFI PZU and PZU regarding limitation of the time for withdrawing cash from the portfolios managed by TFI PZU to at most 3 days after a request for cash is filed;
- keeping open credit facilities in banks and/or the possibility of performing sell-buy-back transactions on treasury securities, including those held until maturity;
- centralization of management of portfolios/funds by TFI PZU;
- limits of liquidity ratios in the banks belonging to the PZU Group.
Credit risk and concentration risk
Credit risk is understood as the risk of a loss or an adverse change in the financial situation resulting from fluctuations in the reliability and creditworthiness of issuers of securities, counterparties and all debtors. It materializes in the form of a counterparty’s default on a liability or an increase in credit spread. The following risk categories are distinguished in terms of credit risk:
- spread risk;
- counterparty default risk;
- credit risk in financial insurance.
Concentration risk is understood as the possibility of incurring loss stemming either from lack of diversification in the asset portfolio or from large exposure to default risk by a single issuer of securities or a group of related issuers.
Credit risk and concentration risk are identified at the stage of making a decision on an investment in a new type of financial instrument or on accepting credit exposure. It involves an analysis of whether the contemplated investment entails credit risk or concentration risk, what its level depends on and what its volatility over time is. Actual and potential sources of credit risk and concentration risk are identified.
Underwriting consists of estimating the probability of risk materialization and the potential impact exerted by risk materialization on a given entity’s financial standing.
The measurement of credit risk is performed using:
- measures of exposure (gross and net credit exposure and maturity-weighted net credit exposure),
- capital requirement calculated using the standard formula.
Concentration risk for a single entity is calculated using the standard formula.
A measure of total concentration risk is the sum of concentration risks for all entities treated separately. In the case of related parties, concentration risk is calculated for all related parties jointly.
In the case of banking entities suitable measures are employed in accordance with the regulations applicable to this sector and best market practices. Credit risk is measured using a set of loan portfolio quality metrics.
Monitoring and control of credit risk and concentration risk involves an analysis of the current risk level, assessment of creditworthiness and calculation of the degree of utilization of existing limits. Such monitoring is performed, without limitation, on a daily and monthly basis.
The monitoring pertains to:
- exposures to financial insurance,
- exposures to reinsurance,
- exposure limits and VaR limits,
- loan exposures (in the case of banking entities).
Reporting involves providing information on the levels of credit risk and concentration risk and the effects of monitoring and control. The frequency of each report and the scope of information provided therein are tailored to the information needs at each decision-making level.
Management actions in respect of credit risk and concentration risk involve in particular:
- setting limits to curtail exposure to a single entity, group of entities, sectors or countries;
- diversification of the portfolio of assets and financial insurance, especially with regard to country and sector;
- acceptance of collateral;
- execution of transactions to mitigate credit risk, i.e. selling a financial instrument, closing a derivative, purchasing a hedging derivative, restructuring a debt;
- reinsurance of the financial insurance portfolio.
The structure of credit risk limits and concentration risk limits for various issuers is established by appointed committees in such a manner that the limits are consistent with the adopted risk tolerance determined by the management boards of the respective subsidiaries and in such a manner that they make it possible to minimize the risk of ‘infection’ between concentrated exposures.
In banking activity the provision of credit products is accomplished in accordance with loan granting methodologies appropriate for a given client segment and type of product. The assessment of a client’s creditworthiness preceding a credit decision is performed using tools devised to support the credit process, including a scoring or rating system, external information and the internal databases of a given PZU Group bank. Credit products are granted in accordance with the binding operational procedures stating the relevant actions performed in the lending process, the units responsible for that and the tools used.
The structure of credit risk limits and concentration risk limits for various issuers is established by dedicated committees in such a manner that the limits are consistent with the adopted risk tolerance determined by the management boards of the individual subsidiaries and in such a manner that they make it possible to minimize the risk of ‘infection’ between concentrated exposures.
In banking activity the provision of credit products is accomplished in accordance with loan granting methodologies appropriate for a given client segment and type of product. The assessment of a client’s creditworthiness preceding a credit decision is performed using tools devised to support the credit process, including a scoring or rating system, external information and the internal databases of a given PZU Group bank. Credit products are granted in accordance with the binding operational procedures stating the relevant actions performed in the lending process, the units responsible for that and the tools used.
In the PZU Group insurance segment, in the credit risk area, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic was low; just like in 2019, no indications of impairment were identified in the portfolio, hence no exposure was classified to basket 3 (instruments for which impairment has been recognized). During 2020 the structure of the financial instruments held changed significantly; the share of corporate exposures, which in principle are characterized by higher risk parameters (PD, LGD), was reduced in favor of purchase of Polish treasury bonds or bonds guaranteed by the State Treasury. The value of the impairment losses in the portfolio in 2020 dropped relative to 2019 due to the change of the portfolio structure to a safer one, shift of the rating structure associated with the overall improvement of the financial results of the entities, and improvement of internal macroeconomic forecasts for Poland relative to the negative scenarios associated with the COVID-19 pandemic from Q1. Reduction of the impairment losses in the portfolio resulted from a decrease of the losses in basket 1, partly balanced by an increase of the losses in basket 2 (instruments with identified significant increase in credit risk according to IFRS 9). As a result of the increase of the portfolio value and decrease of cumulative impairment losses, the coverage with impairment losses, understood as the ratio of cumulative credit risk impairment losses to the gross carrying amount of all PZU Group assets exposed to credit risk subject to the IFRS9 regime, decreased.
From April 2020, no impact of COVID-19 on the increase of the loss ratio in the insurance guarantee portfolio was confirmed. The standing of individual clients is monitored on an ongoing basis.
Operational risk
Operational risk is the risk of suffering a loss resulting from improper or erroneous internal processes, human activities, system failures or external events.
Operational risk is identified in particular by:
- accumulation and analysis of information on operational risk incidents and the reasons for their occurrence,
- self-assessment of operational risk,
- scenario analysis.
Operational risk is assessed and measured by:
- calculating the effects of the occurrence of operational risk incidents,
- estimating the effects of potential operational risk incidents that may occur in the business.
Both banks in the PZU Group, upon KNF’s consent, apply advanced individual models to measure operational risk and to estimate capital requirements on account of this risk.
Monitoring and control of operational risk is supported mainly by an established system of operational risk indicators and limits enabling assessment of changes in the level of operational risk over time and assessment of factors that affect the level of this risk in the business.
Reporting involves communicating to the various decision-making levels information concerning the level of operational risk and the results of monitoring and controlling it. The frequency of each report and the scope of information provided therein are tailored to the information needs at each decision-making level.
Management actions involving reactions to any identified and assessed operational risks involve primarily:
- taking actions aimed at minimizing risks, for instance by strengthening the internal control system;
- risk transfer – in particular, by entering into insurance agreements;
- risk avoidance by refraining from undertaking or withdrawing from a particular type of business in cases where too high a level of operational risk is ascertained and where the costs involved in risk mitigation are unreasonable;
- risk acceptance – approval of consequences of a possible realization of operational risk unless they threaten to exceed the operational risk tolerance level.
Business Continuity Plans in the PZU Group are regularly tested and, consequently, updated.
PZU and PZU Życie implemented solutions and processes to minimize the risk of infection and spread of the coronavirus in the organization. Appropriate safety measures were applied:
- information measures (newsletters, alerts, SMS, information posted in the PZU24 service, webinar, FAQ);
- organizational and legal measures (appointing the Crisis Management Team and its regular meetings, declaring a crisis situation, introducing remote work procedure and mode, updating the Business Continuity Plan, creating a register of identified infections, prevention regarding work contacts, increased personal hygiene standards);
- technical measures (purchase and expansion of hardware increasing the VPN limit, purchase of licenses for the use of online communicators and for software supporting remote work, increasing the phone data transmission limits, equipping employees with notebooks and desktops for remote work, increasing the bandwidth of internet lines);
- protection measures (equipping PZU branches with disinfectants and protective measures, equipping workstations in PZU branches with protective screens, purchase of facemasks and gloves, disinfection and ozoning of rooms).
At each meeting of the Crisis Management Team, the Security Department presented reports on the number of infections among employees and in Poland, work organization in PZU Group companies, availability of the branches and the agency network, execution of orders for personal protective equipment and disinfectants, and expenditures incurred from the Crisis Management Team budget.
The Business Continuity Plans launched in connection with the pandemic in the remaining PZU Group companies operated in accordance with the internal regulations and procedures in place in such companies.
Despite the crisis situation, there were no major disruptions in any PZU Group companies associated with continuity of operation or client service.
Model risk
Model risk, classified by the PZU Group as significant, is defined as the risk of incurring financial losses, incorrectly estimating data reported to the regulatory authority, taking incorrect decision or losing reputation as a result of errors in the development, implementation or application of models.
The formal identification and assessment process for this risk is currently being developed in PZU and PZU Życie. The process aims to ensure high quality of model risk management practices.
The model risk management process involves:
- risk identification, which takes place through regular identification of the models used in the areas covered by the process; identified models are assessed for materiality;
- risk measurement, which is based on the results of independent model validations and monitoring;
- risk monitoring, which involves ongoing analysis of deviations from the adopted points of reference regarding the model risk (e.g. verification of the recommendation execution method and comparison of the risk level to the adopted tolerance level);
- risk reporting, which involves communicating the process results on the appropriate management level, in particular results of risk monitoring, validation and measurement;
- management actions, which aim to mitigate the model risk level; they can be active (e.g. recommendations resulting from completed validations) and passive (developing model and model risk management standards).
In the entities from the banking sector, given the high significance of model risk, the management of this risk has already been implemented for some years in the course of adaptation to the requirements of Recommendation W issued by the KNF. Both PZU Group banks have defined standards for the model risk management process, including the rules for developing models and evaluating the quality of their operation, ensuring at the same time appropriate corporate governance solutions.
Compliance risk
Compliance risk is the risk that PZU Group entities or persons related to PZU Group entities may fail to adhere to the applicable provisions of law, internal regulations or standards of conduct, including ethical standards, adopted by PZU Group entities, and the risk of violating these provisions of law, regulations and standards. This results or may result in:
- legal sanctions incurred by the PZU Group or persons acting on its behalf,
- financial losses,
- loss of reputation or credibility.
PZU makes efforts aimed at ensuring adequate and uniform standards of compliance solutions in all subsidiaries and monitors compliance risk throughout the entire Group.
In 2020 the PZU Group entities had compliance systems adapted to the standards designated by PZU.
The provision of full information on compliance risk in Group companies is the responsibility of their compliance units. They are required to assess and measure compliance risk and take appropriate remedial actions aimed at mitigating the likelihood of realization of this risk.
PZU Group entities are obligated to provide ongoing information on compliance risk to the PZU Compliance Department. The tasks of the Compliance Department include, among others:
- analysis of monthly and quarterly reports received from compliance units of each member of the Group,
- assessment of the impact of compliance risk on the PZU Group as a whole,
- analysis of the implementation of recommendations issued to entities pertaining to the fulfillment of the compliance function,
- support of the PZU Group entities’ compliance business units when assessing compliance risk,
- reporting to the PZU Management Board and Supervisory Board.
Compliance risk includes, in particular, the risk that the operations performed by PZU Group entities will be out of line with the changing legal environment. This risk may materialize as a result of delayed implementation or absence of clear and unambiguous laws, or what is known as a legal gap. This may cause irregularities in the PZU Group’s business and, as a result, lead to higher costs (for instance, administrative penalties, other financial penalties) and a heightened level of loss of reputation risk.
Due to the broad spectrum of the PZU Group’s business, reputation risk is also affected by the risk of litigation is predominantly inherent in the Group’s insurance companies and banks.
The identification and assessment of compliance risk for each internal process in PZU Group entities is the responsibility of the heads of organizational units, in accordance with the allocation of responsibility for reporting. Moreover, compliance units in PZU Group entities identify compliance risk on the basis of notifications to the register of conflicts of interest, gifts and irregularities, and from inquiries sent to them.
Compliance risk is assessed and measured by calculating the effects of risk materialization of the following types:
- financial risks, resulting among others from administrative penalties, court judgments, decisions issued by UOKiK, contractual penalties and damages,
- intangible risks pertaining to a loss of reputation, including damage to the PZU Group’s image and brand.
Compliance risk is monitored through:
- systemic analysis of the regular reports received from the heads of organizational units and cells;
- monitoring of regulatory requirements and adaptation of the business to the changing legal environment of PZU Group entities;
- participation in the legislative work on amendments to generally prevailing provisions of law;
- performing diverse activities in industry organizations;
- coordination of external control processes;
- monitoring of implementation of recommendations issued following internal audits;
- coordination of the fulfillment of reporting duties imposed by the stock exchange (in respect of PZU) and by statute;
- popularization of knowledge on competition law and consumer protection among PZU Group employees, according the area of their activities;
- monitoring of anti-monopoly jurisprudence and proceedings conducted by the President of UOKiK;
- reviews of the implementation of recommendations issued by the PZU Group’s compliance unit;
- ensuring uniform standards and consistent implementation of the compliance function within the PZU Group.
Management actions in response to compliance risk include in particular:
- acceptance of the risk arising, without limitation, from legal and regulatory changes;
- mitigation of the risk, including by: adjustment of procedures and processes to changing regulatory requirements, evaluation and design of internal regulations to suit compliance needs, participation in the process of agreeing on marketing activities;
- avoidance of risk by preventing any involvement of PZU Group entities in activities that are out of compliance with the applicable regulatory requirements, best market practices or activities that may have an unfavorable impact on the PZU Group’s image.
As part of efforts aimed at reducing compliance risk in the PZU Group at system level and day-to-day level, the following risk mitigation actions are undertaken:
- continuous implementation of an effective compliance function as a key management function;
- participation in consultations with legislative and regulatory authorities (supervised entities within the PZU Group) at the stage of development of the regulations (social consultations);
- delegating representatives of the PZU Group’s supervised entities to participate in the work of various commissions of regulatory authorities;
- participation in implementation projects for new regulations;
- training of staff on new regulations, standards of conduct and recommended management actions;
- issuing opinions on internal regulations and recommending possible amendments to ensure compliance with the applicable laws and accepted standards of conduct;
- verifying procedures and processes in the context of their compliance with the applicable laws and accepted standards of conduct;
- aligning documentation to upcoming changes in legal requirements before they are enacted;
- systemic supervision exercised by PZU over the execution of the compliance function in PZU Group entities;
- analyses and ongoing monitoring of the application of “Chinese wall” rules – in connection with the additional investor commitments made by PZU in connection with the proceedings under the notification on the intent to purchase Bank Pekao’s shares;
- ongoing monitoring of changes in the legal and regulatory environment in order to identify gaps or areas requiring action to ensure compliance.
The actions in 2020 in the compliance area were also associated with the PZU Group continuing to meet the criteria for treating it as a financial conglomerate, and hence applying supplementary oversight to it under the Act of 15 April 2005 on supplementary oversight over credit institutions and insurance undertakings, reinsurance undertakings and investment firms comprising a financial conglomerate. The compliance area was involved in the work to align the Company to the requirements ensuing from this act, as well as to the requirements stemming chiefly from the following legal acts:
- Directive of 15 May 2014 on Markets in Financial Instruments (MIFID II) (this regulation is material for some PZU Group entities, in particular for TFI);
- Act of 1 March 2018 on Combating Money Laundering and Financing of Terrorism;
- Act of 16 October 2019 on amending the Act on Public Offerings and the Conditions for Offering Financial Instruments in an Organized Trading System and on Public Companies and some other acts;
- International Financial Reporting Standard 17 “Insurance Contracts” (IFRS 17);
- draft Act Amending the Mandatory Insurance, Insurance Guarantee Fund and Polish Motor Insurers' Bureau Act and the Insurance and Reinsurance Activity Act;
- draft act amending the Commercial Company Code and certain other acts;
- Directive (EU) 2019/1937 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2019 on the protection of persons who report breaches of Union law;
- Regulation (EU) 2019/2088 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 November 2019 on sustainabilityrelated disclosures in the financial services sector, entered into force;
- Regulation (EU) 2020/852 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 June 2020 on the establishment of a framework to facilitate sustainable investment, amending Regulation (EU) 2019/2088;
- Act of 16 April 2020 on Special Support Instruments in Connection with the Spread of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus (the so-called Anti-crisis Shield 2.0).
Risk concentration
When managing the various categories of risk, the PZU Group identifies, measures and monitors risk concentration. Compliance with the regulatory obligations imposed on groups identified as financial conglomerates is supported by the model introduced in 2020 to manage significant risk concentration in the PZU Financial Conglomerate in keeping with the requirements of the Supplementary Oversight Act.
Supplementary supervision protects the financial stability of lending institutions, insurance undertakings, reinsurance undertakings and investment firms being members of financial conglomerates. The supervision is exercised, among others, through measuring the risk concentration level in the financial conglomerate as a whole, also from the perspective of regulated entities being its members.
The implementation of this model served the purpose of defining the risk concentration management principles and supporting the units involved in the process, in particular through:
- defining the roles and responsibilities of individual participants of the significant risk concentration management process;
- introducing consistent risk definitions;
- introducing the principles of identifying, measuring and assessing risk;
- defining the risk limits and threshold values;
- defining the principles of monitoring significant risk concentrations;
- introducing the principles of reporting and management decision-making.
Regulated subsidiaries monitor and submit regular reports to the leading entity in the PZU Financial Conglomerate on the measures and data required to identify risk concentrations. In the case of identification of an excessive risk concentration, management actions are implemented on the level of the given entity or the whole financial conglomerate.
Risk concentration is measured and monitored, in particular, in the following dimensions:
- concentration per counterparty or group of counterparties,
- concentration per currency,
- concentration per sector of economy,
- concentration per country,
- concentration per asset type.
